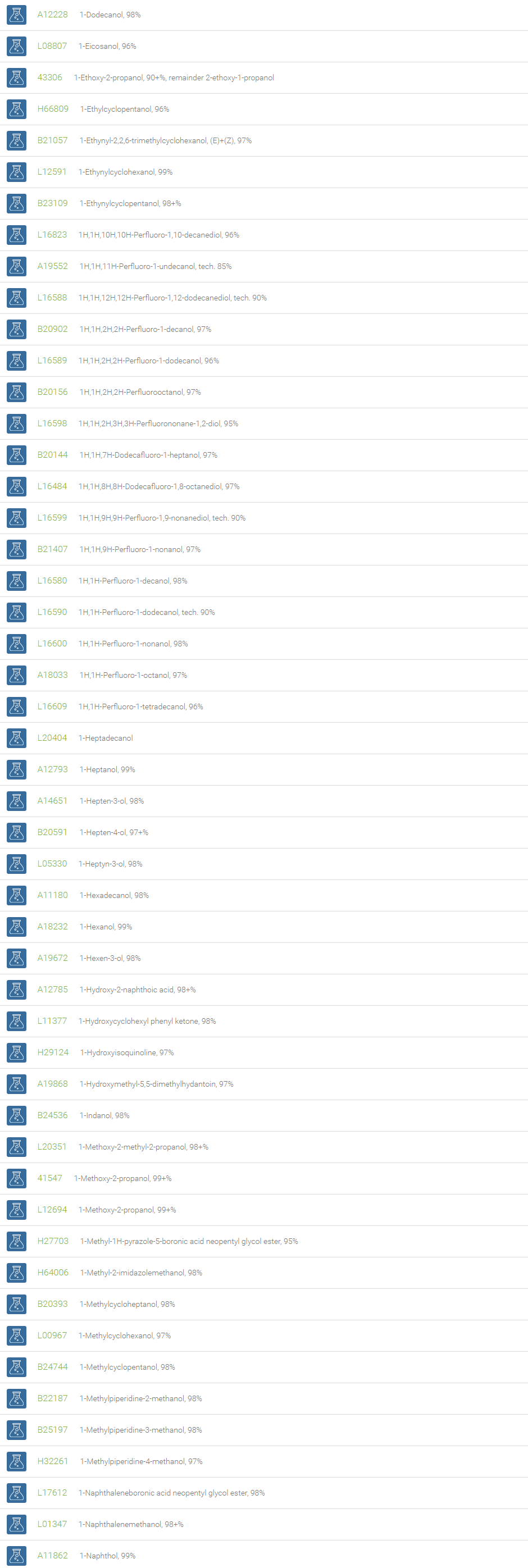
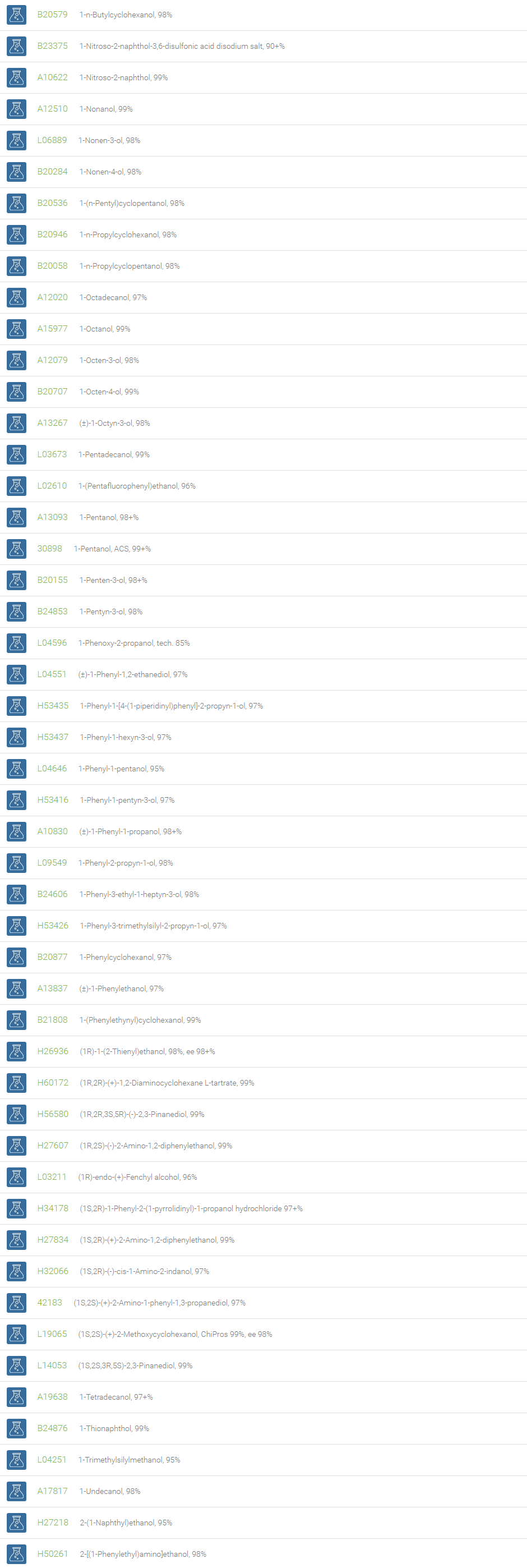
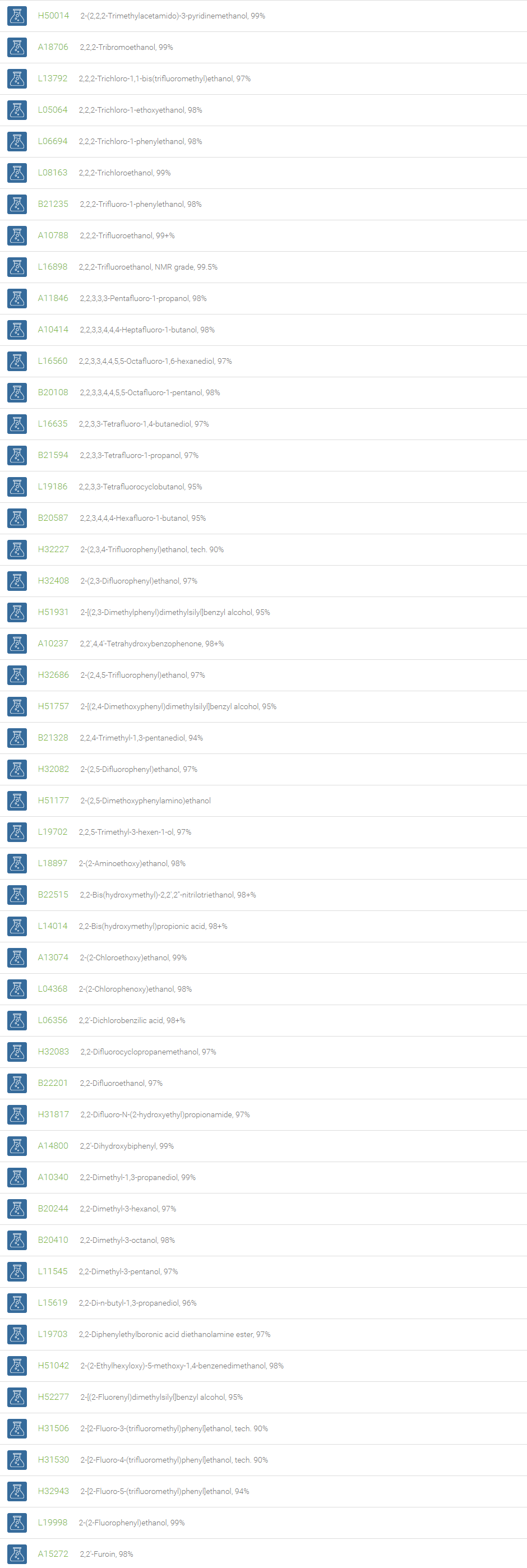
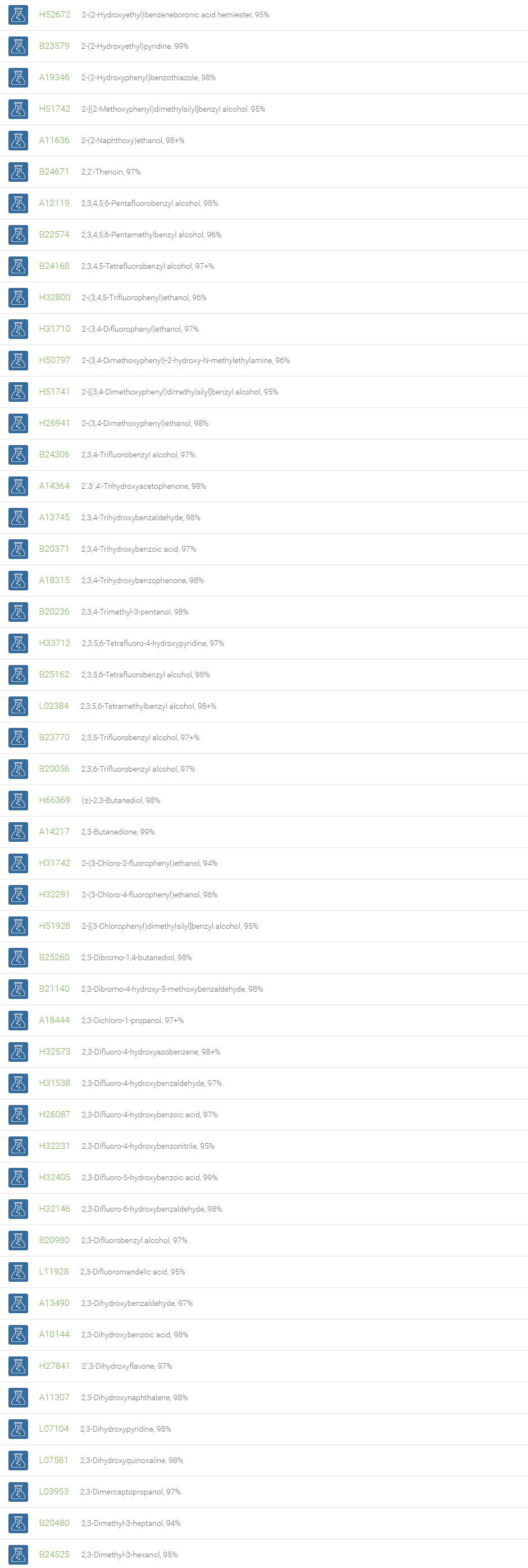
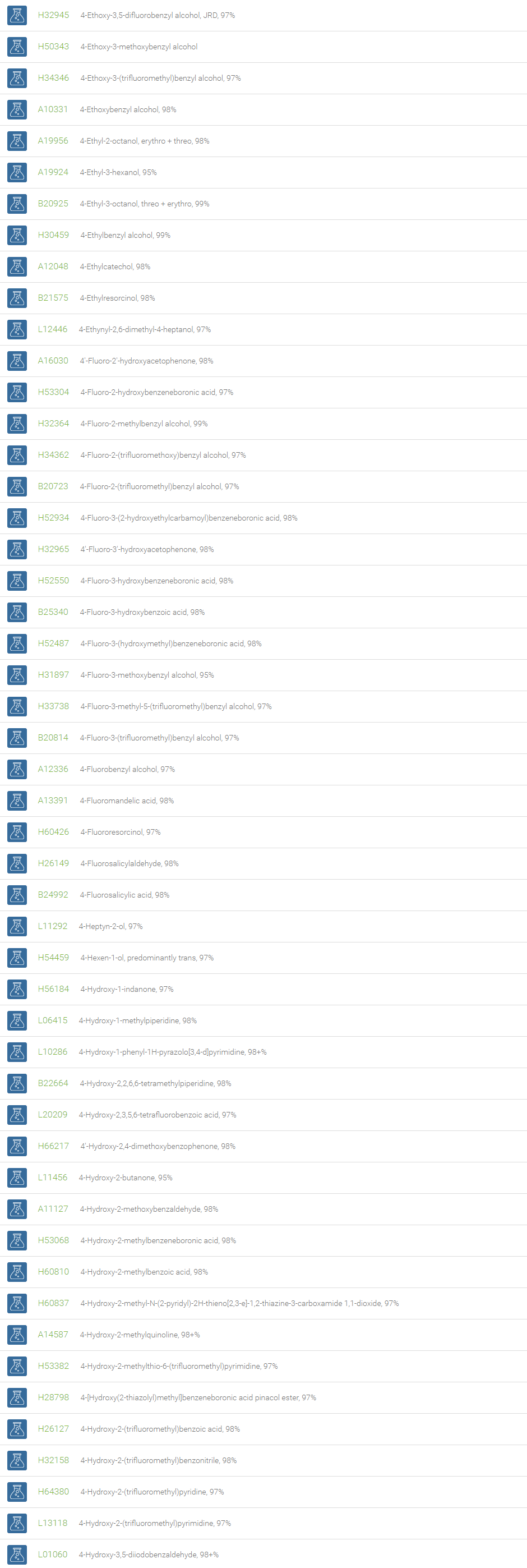
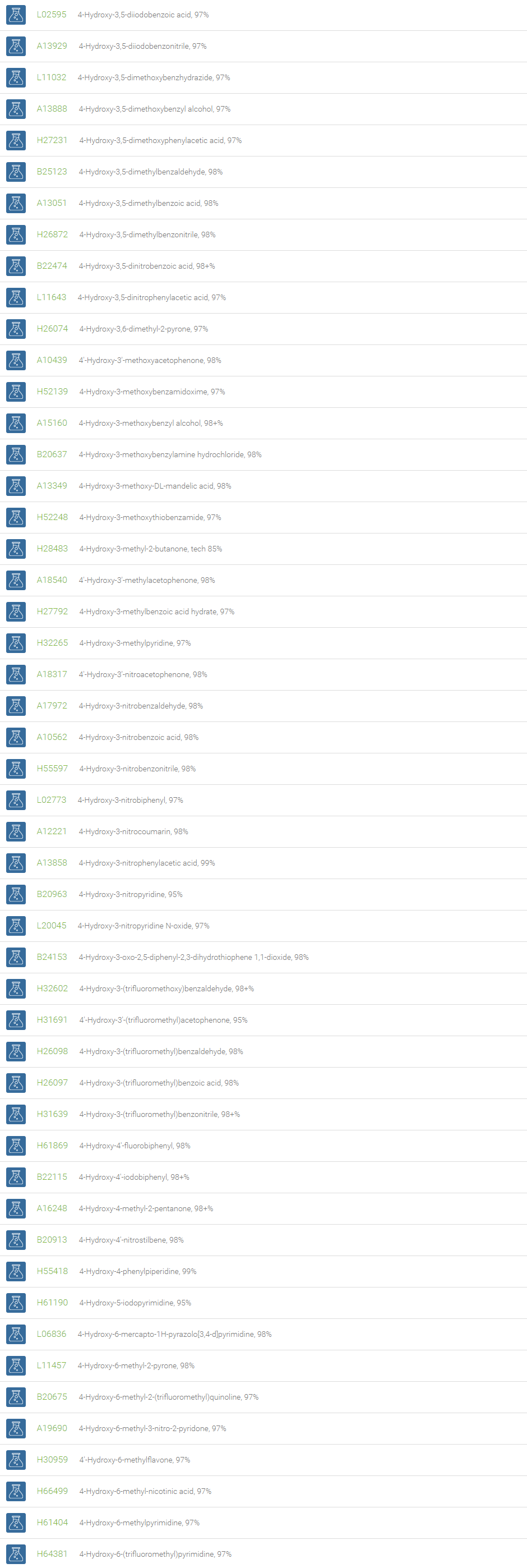
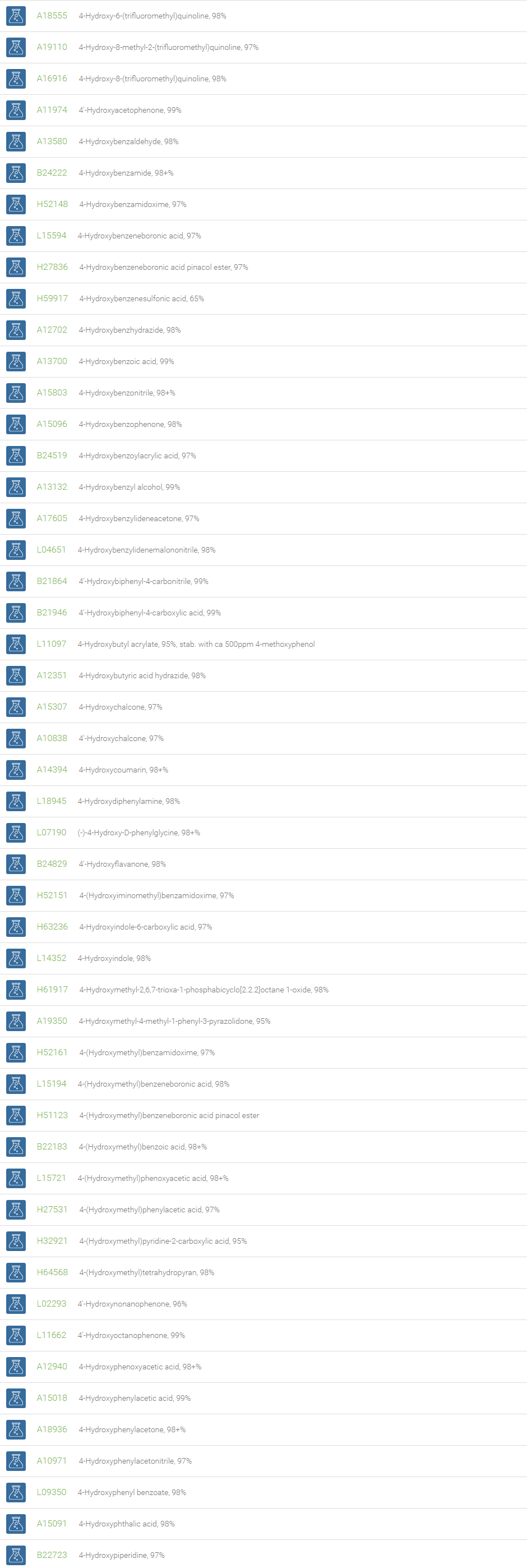
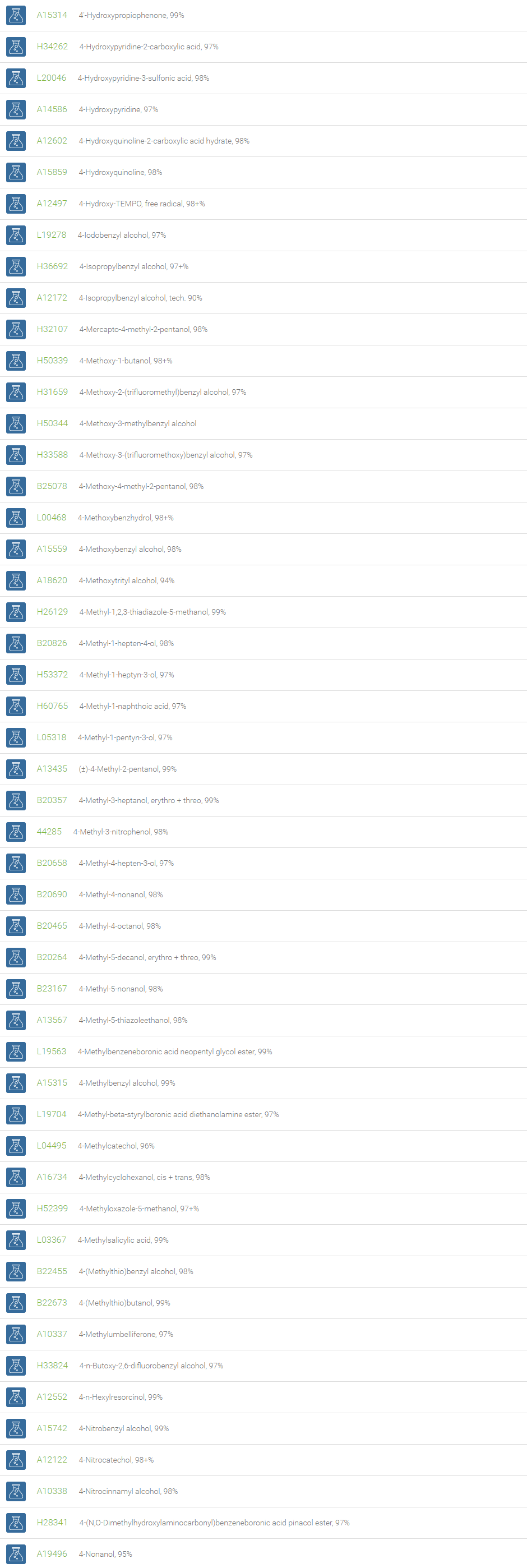
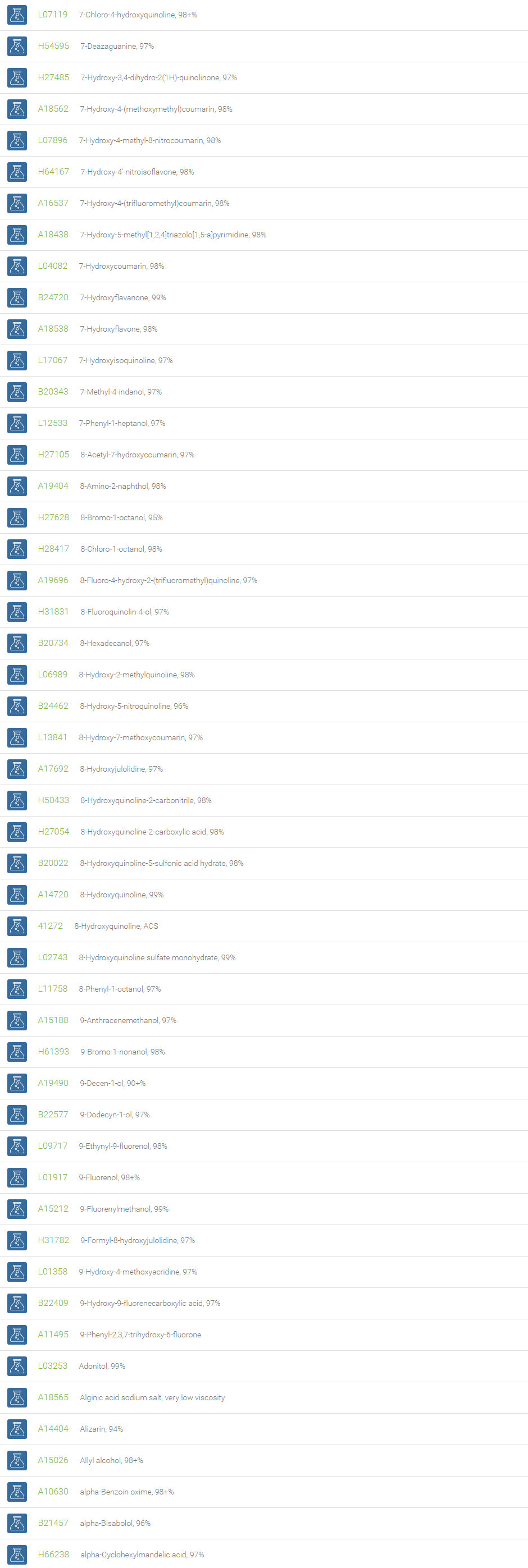
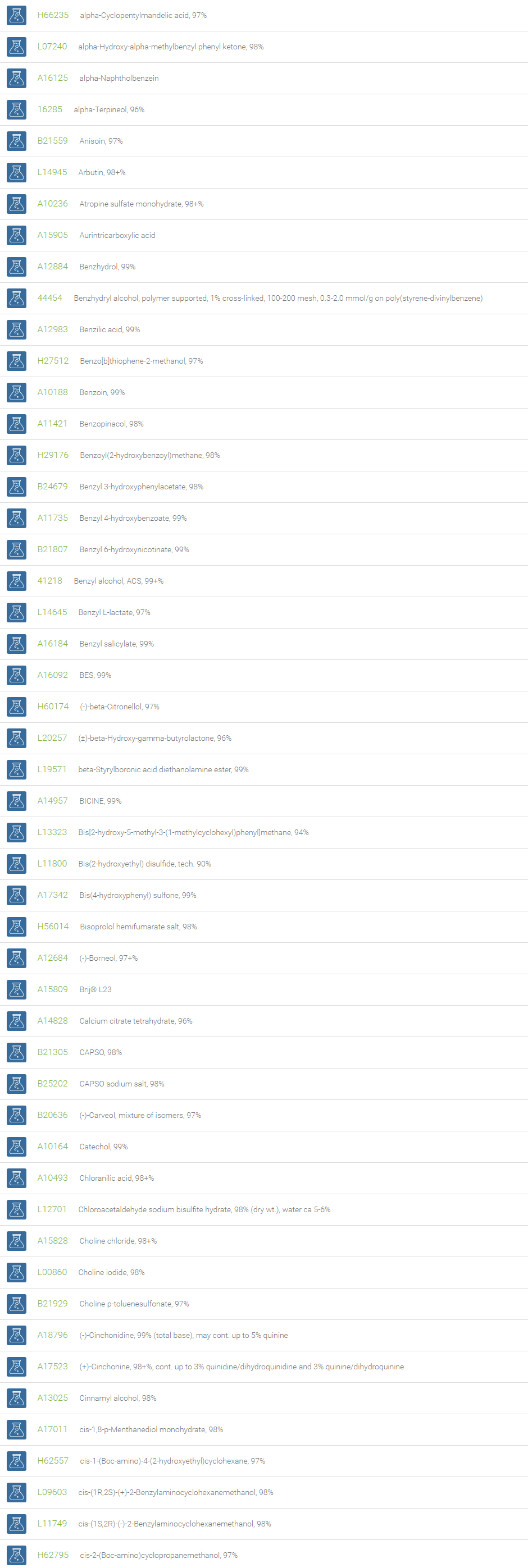
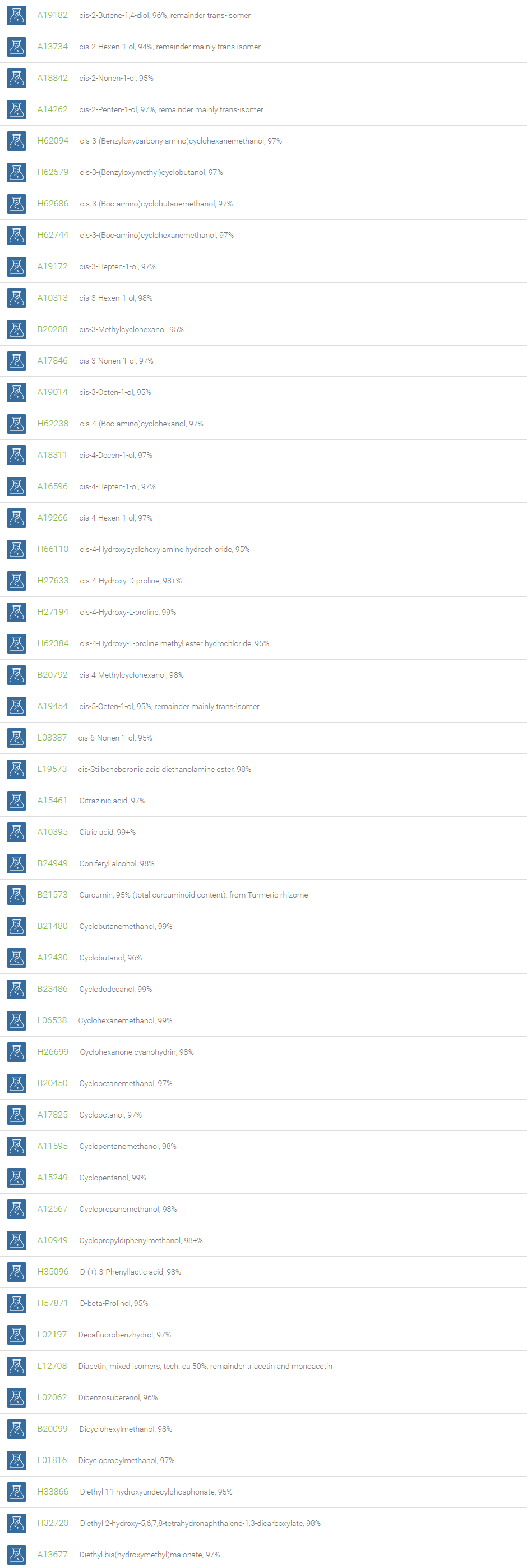
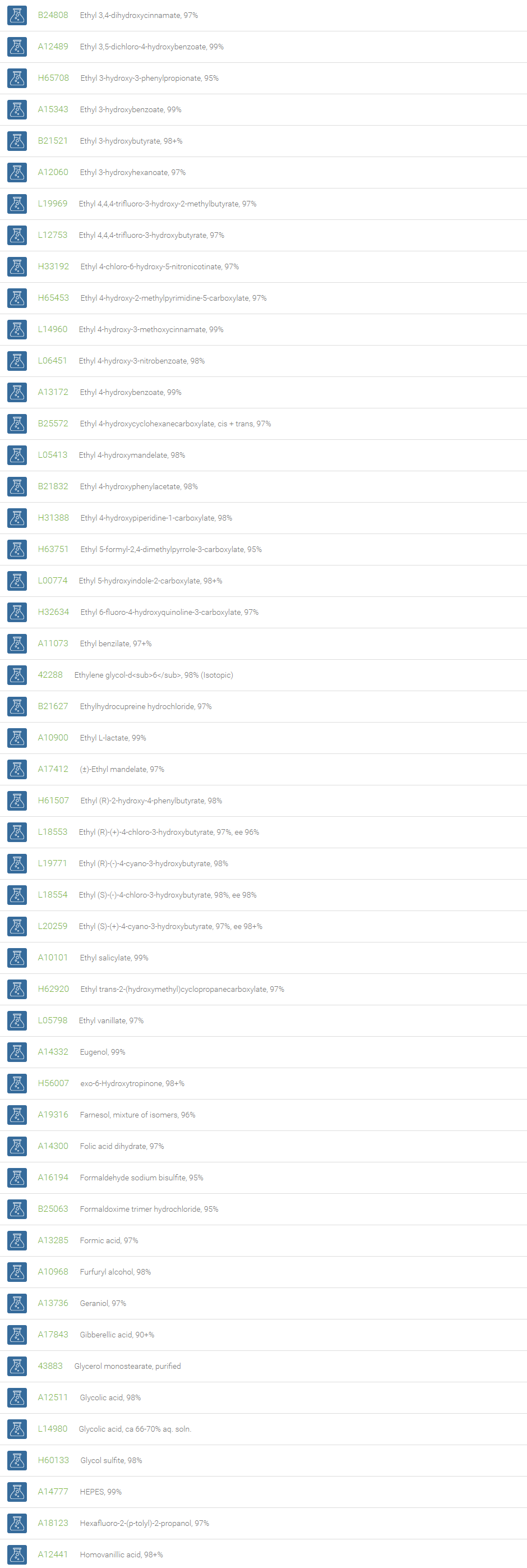
Alcohols

Alcohols
An alcohol is an organic compound in which one of more hydroxyl groups are attached to saturated carbon atoms. Alcohols are normally classified in to different groups such as primary, secondary, and tertiary based on the substitutions of the carbon atom bearing the OH group. The primary, secondary, tertiary alcohols can also be defined by the molecule containing -CH2OH, -CHROH and -CR2OH respectively. Alcohols are reactive and are capable of being converted to metal salts, alkyl halides, esters, aldehydes, ketones, amines, and carboxylic acids. Alcohols can also undergo oxidation; tosylation, esterification, pinacol rearrangement, substitutions to form alkyl halides, dehydration to form alkenes and ethers. This makes them important intermediates and reagents in organic synthesis.
Alcohols are used as solvents in reactions for dissolving chemicals which are insoluble in water, for examples perfumes, vegetable and cosmetic essences like vanilla extracts. One common application for alcohol is in hand sanitizer. There are a number of compounds in which alcohol is the main component, for example, plastics, synthetic fibers, paints, resins, magnetic film, safety glass laminate, adhesives, solvents, carpeting, insulation, refridgerants, windshield washer fluid, particle board, pigments and dyes. Pure methanol can be used as a transportation fuel, a fuel cell hydrogen carrier and also in wastewater denitrification, biodiesel transesterification and electricity generation.