Iodates & Iodites

Iodates & Iodites
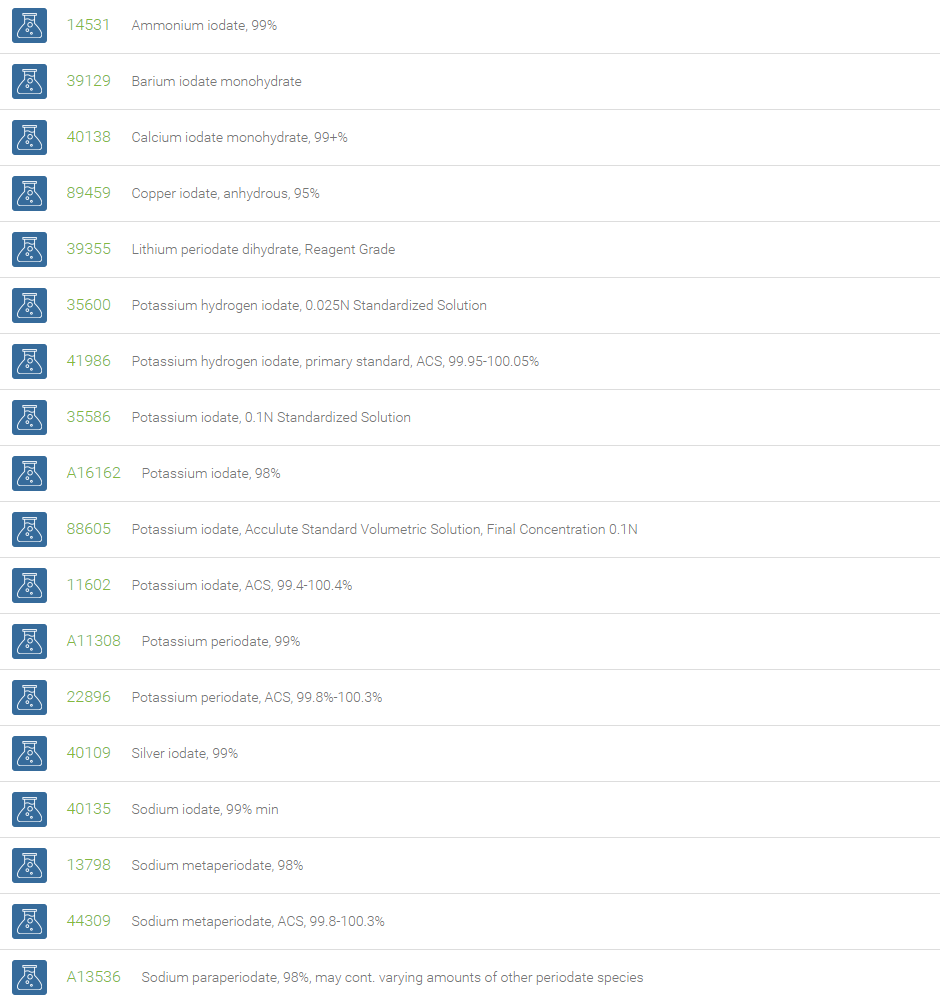
Iodates are a class of chemical compounds containing a IO3– group. An iodate is a conjugate base of iodic acid. Examples are sodium iodate (NaIO3), silver iodate (AgIO3), and calcium iodate (Ca(IO3)2). Potassium hydrogen iodate (KH(IO3)2) is a double salt of potassium iodate and iodic acid. Iodate salts are used in the iodine clock reaction. Potassium iodate has been issued as a prophylaxis against radioiodine absorption, & to protect against accumulation of radioactive iodine in the thyroid.
Iodates are powerful oxidizing agents. Potassium iodate is used as a source for dietary iodine and also an ingredient in some baby formula milk. Sodium iodate is sometimes found as a conditioner in baking ingredients, and is a minute ingredient in table salt. Potassium iodate is highly effective for the treatment of endemic goiter. Calcium iodate is an oxidant added to lotions and ointments as an antiseptic and deodorant. It is also used in the food industry in animal feed, and in the manufacture of disinfectants.
Iodite is an anion composed of iodine and oxygen, with the chemical formula IO2–. In this compound, iodine exists in +3 oxidation state. Iodites are highly unstable and have never been isolated. However they have been detected as intermediates in the conversion between iodide and iodate.