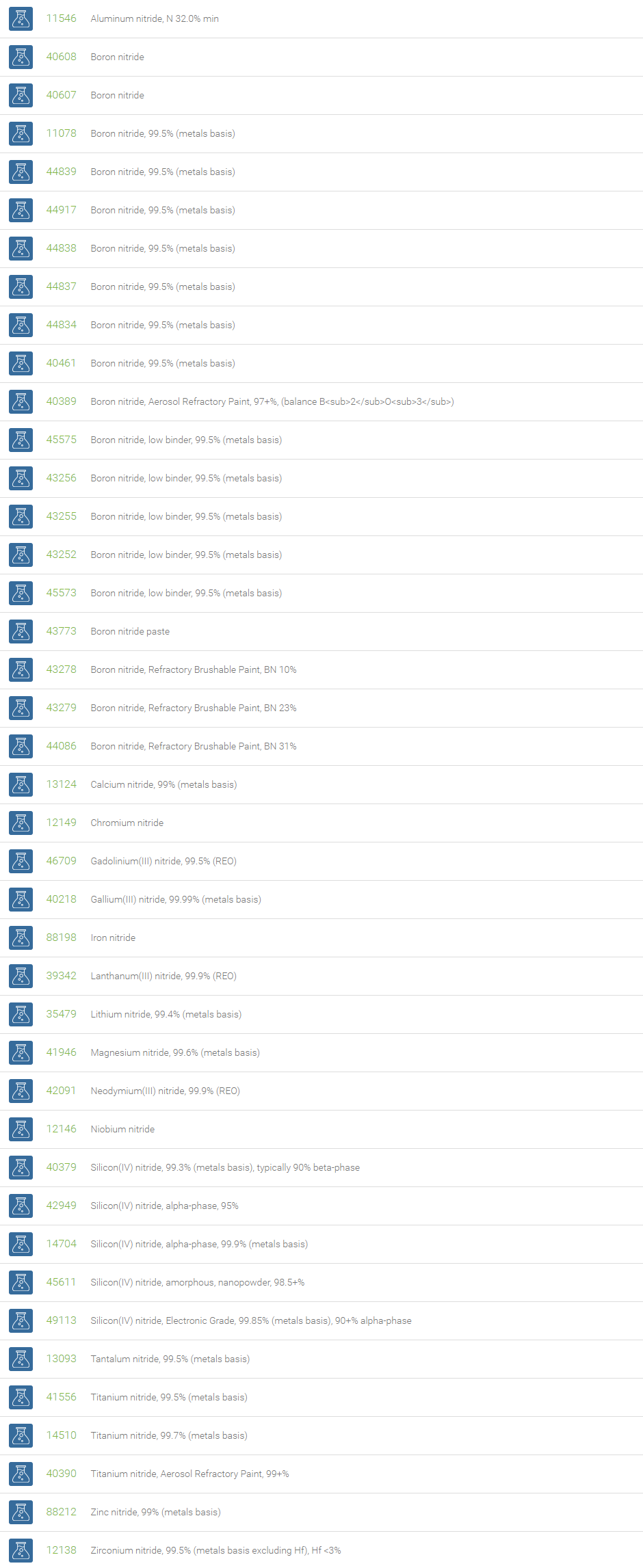
Nitrides

Nitrides
Nitrides are compounds of nitrogen having an oxidation state of 3-. Nitrides can be classified into three general categories: ionic, interstitial, and covalent. Alkali and alkaline earth nitrides are called as ionic nitrides. Alkaline earth nitrides are formed with the formula M3N2 (for example, Ca3N2, Ba3N2, Mg3N2). These compounds undergo hydrolysis to produce ammonia and the metal hydroxide. Transition metal nitrides form compounds with the formula MN, M2N, and M4N. The largest group of nitrides is the interstitial nitrides. These compounds have high melting points. These are extremely hard, and usually have metallic luster and high conductivities. The nitrides of p-block elements are called as covalent nitrides. These have wide range of properties depending on nitrogen bonding (eg., BN,(CN)2,P3N5,S4N4,S2N2).
With strong attraction of the nitride ion towards metal ions and high lattice energy, nitrides are often refractory materials. Nitrides are useful as cutting materials, hard coatings and high-temperature lubricants and are used as insulators or wide bandgap semiconductors. A comprehensive review of the electronic, optical, thermal, mechanical, magnetic, piezoelectric, catalytic, ecological, biological and wetting properties, applications and research perspectives for the novel 2D nanomaterials are discussed in Pakel, A. Nano boron nitride flatland. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 934-959.