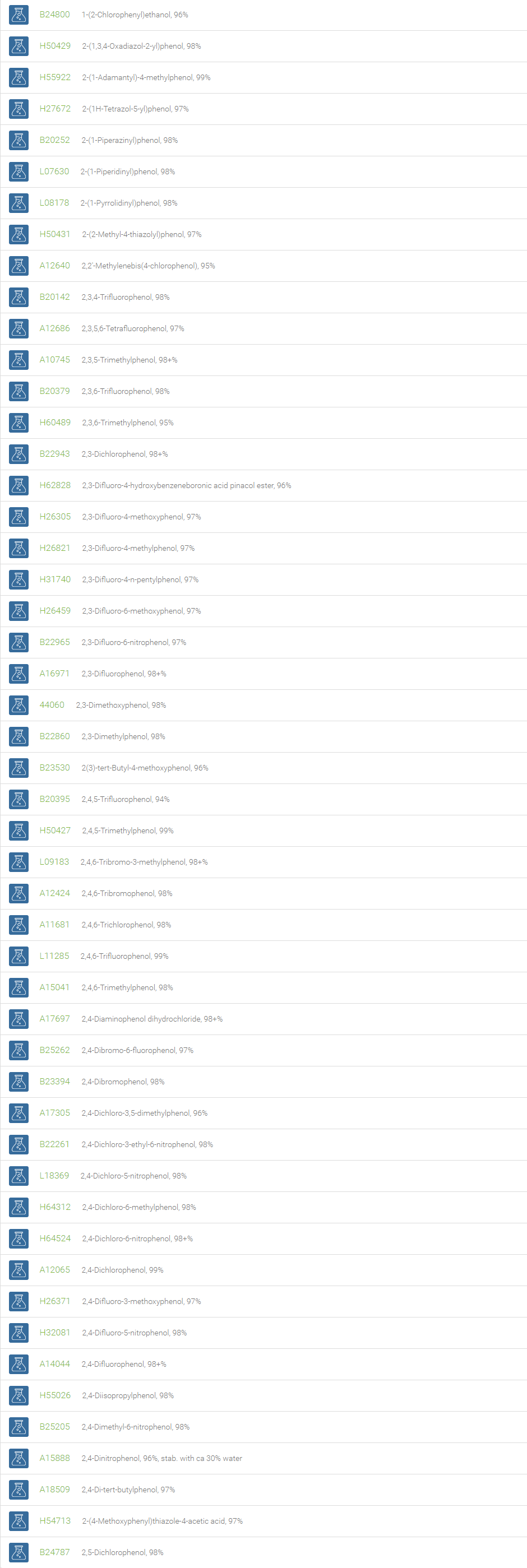
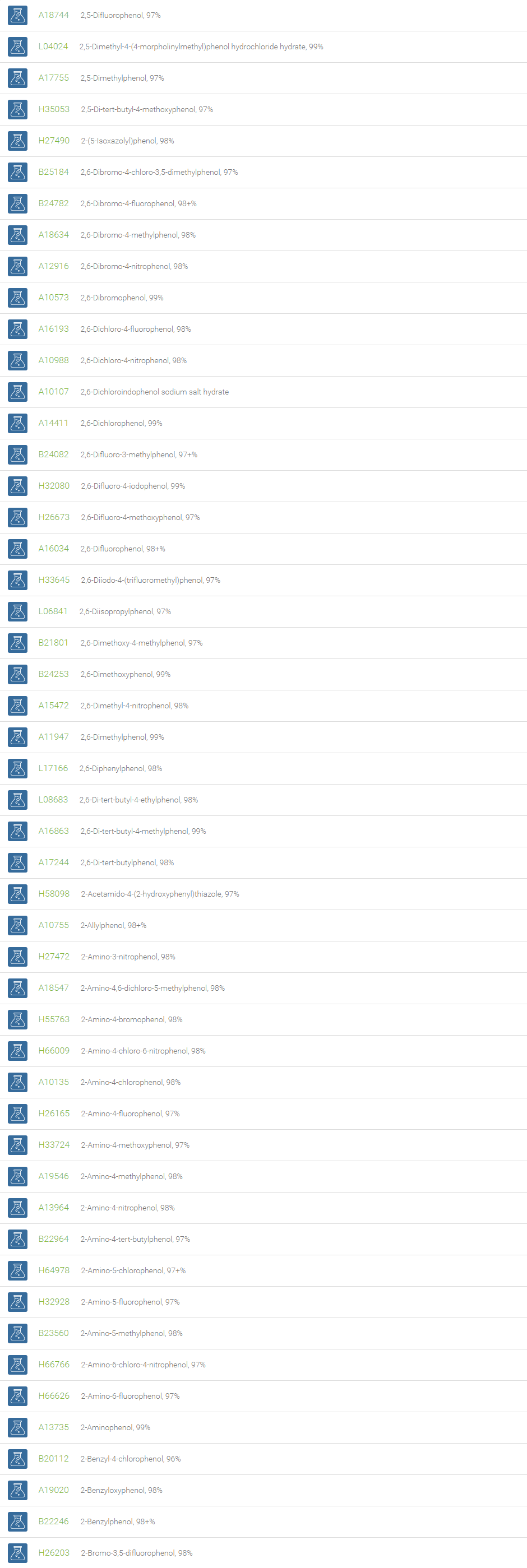
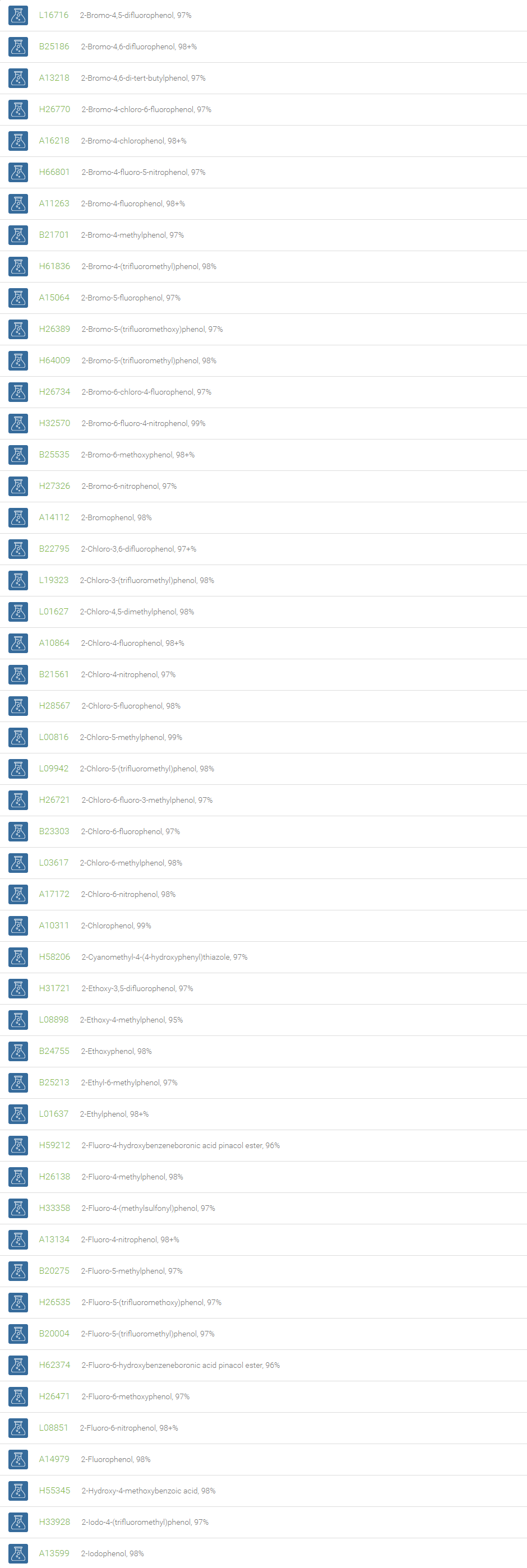
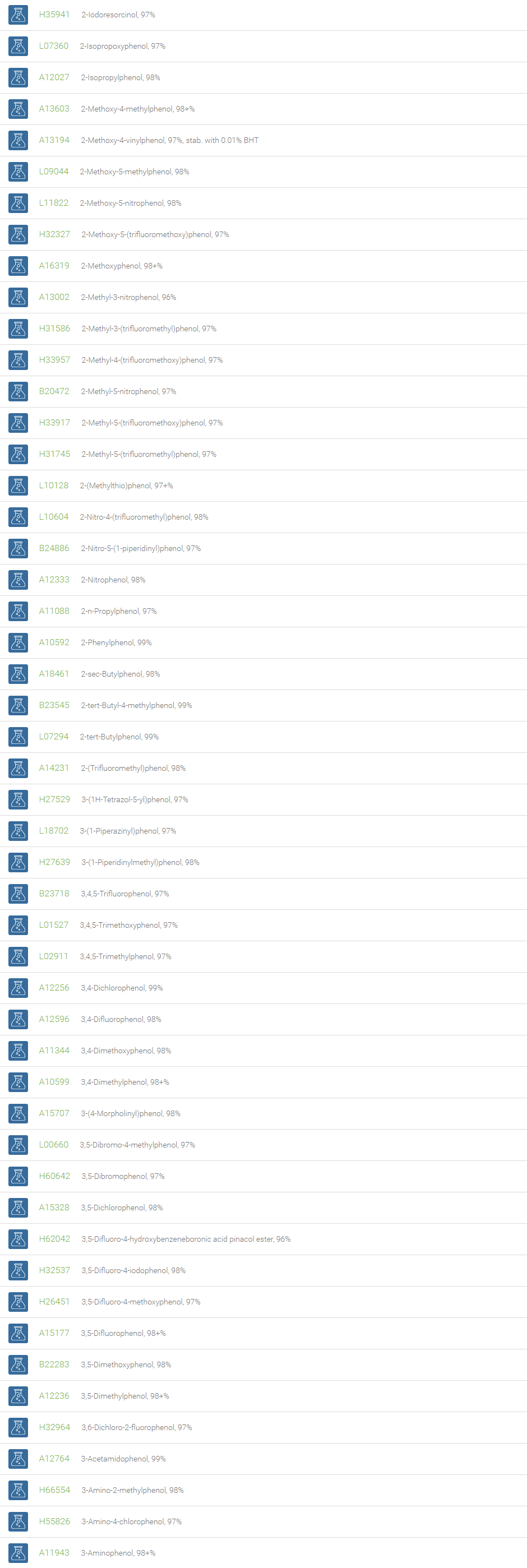
Phenols

Phenols
Organic compounds with a hydroxyl group directly attached to an aromatic carbon atom are called phenols. Depending on the number of phenolic units in the molecule, they are classified as simple phenols and polyphenols. Phenols are efficient partners in a variety of reactions such as electrophilic aromatic substitutions, Bucherer carbazole synthesis and oxidative de-aromatization to quinones in the Teuber reaction.
Phenols are employed in the preparation of resins, dyes, explosives, lubricants, and plastics. Phenol and its derivatives are basic building blocks for polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Phenols are employed in medicinal products such as ear and nose drops, throat lozenges and mouthwashes. The substituted phenols are utilized in the dye industry. Phenol derivatives find use in the preparation of cosmetics comprising sunscreens, hair colourings and skin lightening preparations. Phenols are also wide-spread in nature. Phenols substituted with bulky groups at ortho- positions, like butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), are endowed with antioxidant property and are used as antioxidants in many formulations such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, electrical transformer oil, solvents, and organic reactions.