Quinone

Quinone
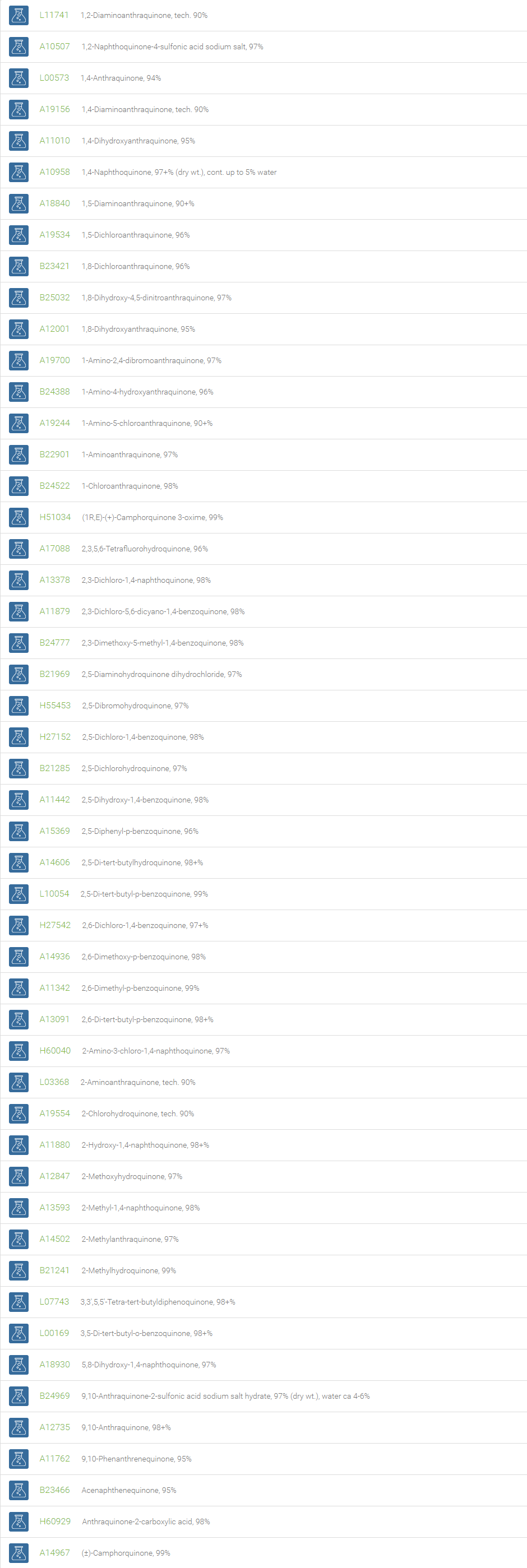
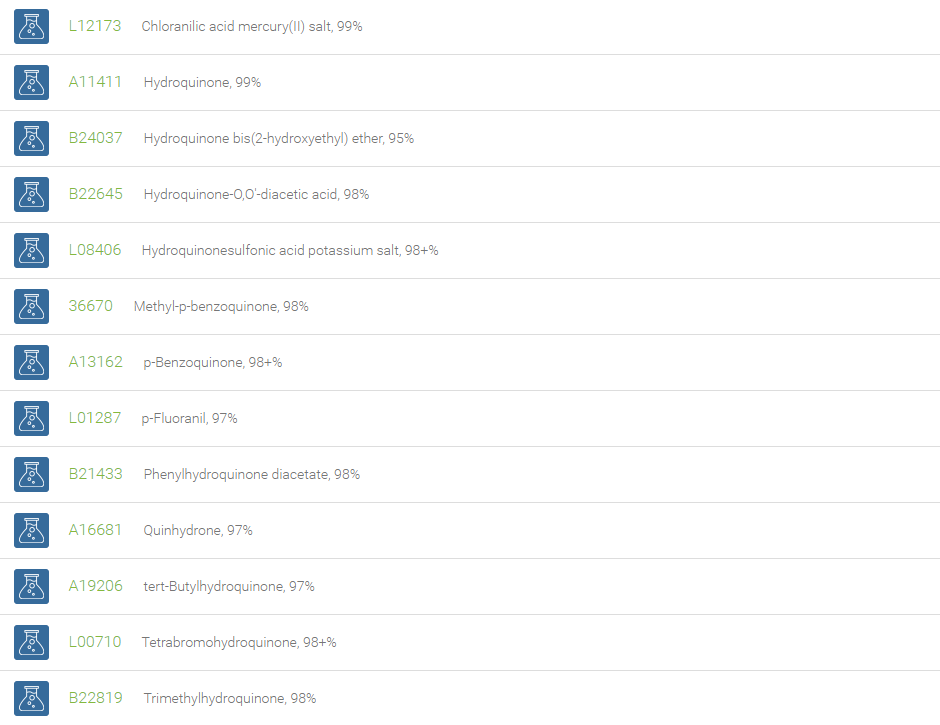
Quinones are any class of cyclic six-membered unsaturated organic compounds that have two carbonyl groups either adjacent or separated by a vinylene group. Examples include 1,4-benzoquinone, 1,2-benzoquinone, 1,4-naphthoquinone, and 9,10-anthraquinone. These coloring substances, both natural and artificial (e.g. dyes and pigments), are made up of basic units of quinone derivatives and hence play a prominent role in dyestuffs. The most distinguishing reaction of quinone is the reduction of the compound to its corresponding dihydroxy form. This feature is utilized in the popular quinhydrone electrode that is used in the determination of hydrogen ion concentration in solutions. Owing to its ability to oxidize, 1,4-benzoquinone is used in the Wacker-type oxidation, wherein the alkene is oxidized to afford the corresponding ketone.
Quinones are used as chemical intermediates, inhibitors of polymerization, oxidizing agents, photographic chemicals, tanning agents and chemical reagents. The quinones are basic subunits, which exhibit prominent pharmacological applications such as antibiotic, antitumor, antimalarial, antineoplastic, and anticoagulant activity. Derivatives of quinones are essential components of biologically relevant molecules such as electron acceptors in electron transport chains, meaning those electron transport chains used in photosynthesis and aerobic respiration. Quinones are used in the large scale industrial production of hydrogen peroxide.