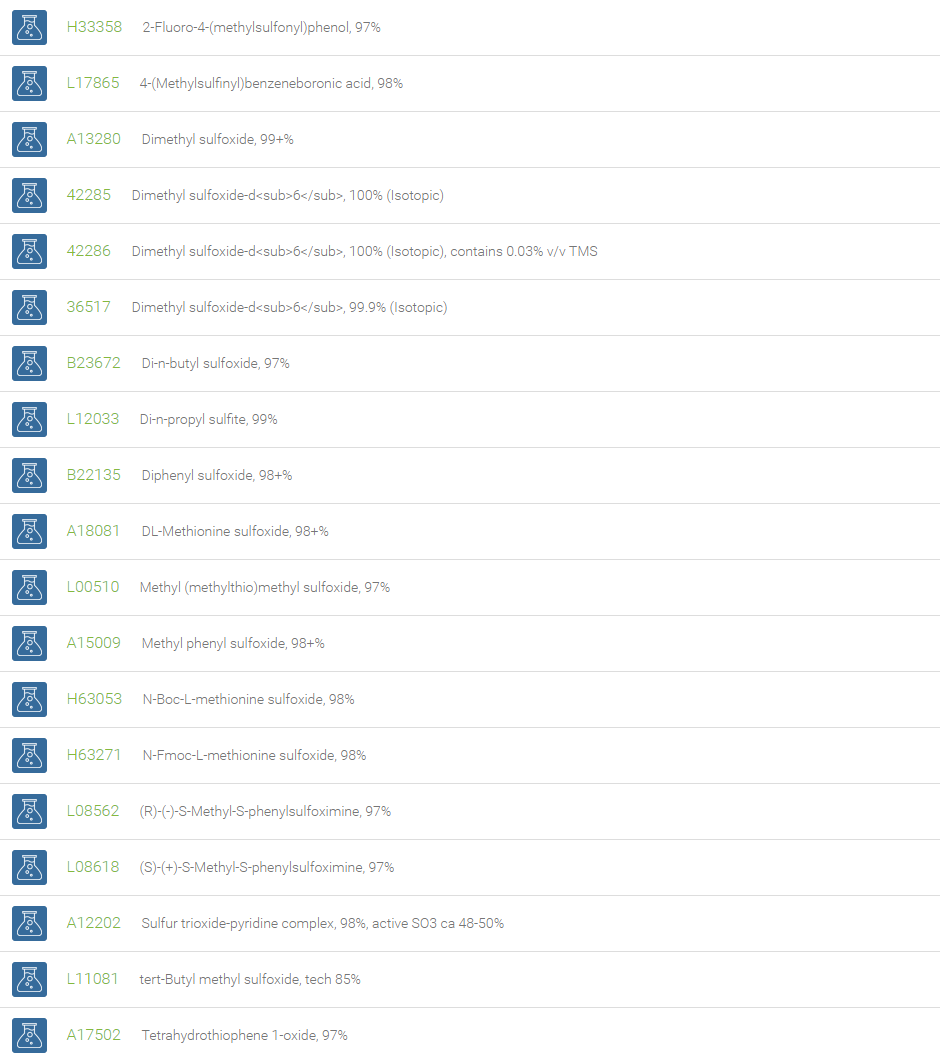
Sulfoxide

Sulfoxide
Sulfoxides are a class of compounds that contains a polar sulfinyl (-SO-) functionality attached to two carbon atoms. Owing to their high electrostatic aspect, sulfoxides have a high dipolar nature with a positive charge on the sulfur atom. Ignoring the lone pair of electrons, sulfoxides assume a trigonal pyramidal geometry. Chirality is associated with sulfoxides containing two different groups attached to the sulfur atom, due to the relatively high energy that is required for inversion, which makes the optical isomers stable. In Organic chemistry, sulfoxides are substrates for the Pummerer rearrangement.
Dimethyl sulfoxide is an important highly polar solvent that is miscible with water and has a low level of toxicity. DMSO has long been used industrially as a reaction solvent for the synthesis of drugs and as an important excipient in finished pharmaceutical dosage forms. DMSO has the ability to penetrate animal tissues and thus finds use as solvent for topically applied drugs and antitoxins. DMSO is also a reagent in a number of oxidation reactions like Swern oxidation and Moffat oxidation.